Why is the UHF-VHF spectrum the preferred band for Remote Rural Broadband Systems (RRBS)?
There are technical, economic, and social grounds, why the spectrum in the UHF range, in particular the TV-WS range should be available for RRBS. See the table below to compare UHF Band versus L/S Band.
What is the difference between clear line of site (LOS) and near line of sight (NLOS)?
Near-line-of-sight (NLOS), sometimes called non-line-of-sight, is radio transmission across a path that is partially obstructed, usually by a physical object in the innermost Fresnel zone. Note, with near line of sight, the wider Fresnel pattern results in many obstructions being accommodated, for example this means loss due to foliage, buildings, and small hills is significantly reduced. Near line of sight also requires a very low Rain Fade and design margins can be 6dB or less.
Clear line of sight (LOS) is radio transmission across a path that is unobstructed. Many types of radio transmissions depend, to varying degrees, on line of sight between the transmitter and receiver.
Both the WiDOX 3.1 and MiLTE solutions operate on near line of sight.
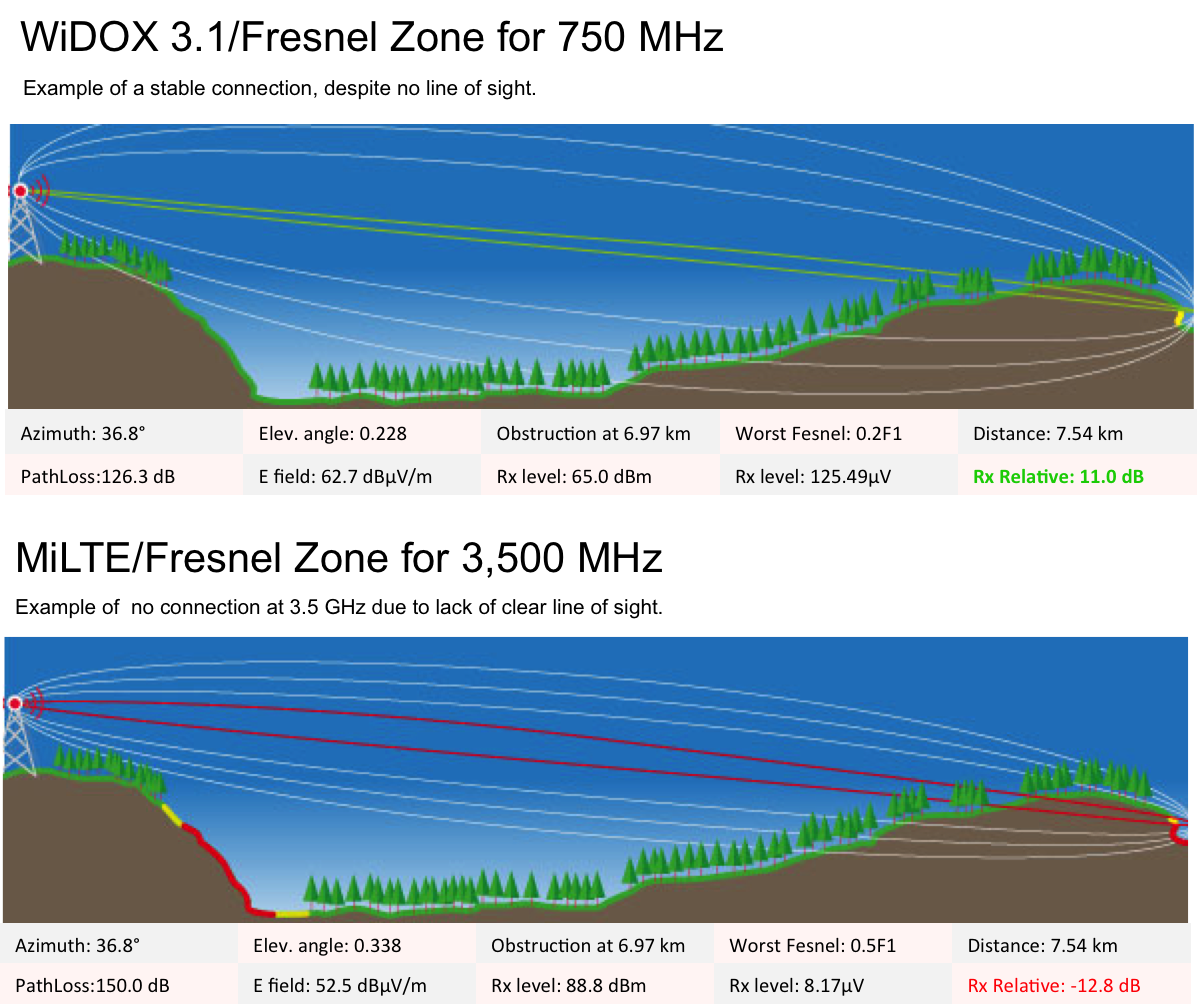
What is the difference between WiDOX 3.1 operating in UHF Band and LTE operating in L/S Band? The picture below shows that at 750 MHz the received signal is 11. dB and at 3,500 MHz the received signal is -12.8 dB. So the system operating at 750 MHz can have clients behind the hill and they connect, but at 3,500 MHz they will not be able to connect. This basically shows that at lower frequency 750 MHz even clients that have obstructions in front of them still are able to connect. The UHF frequencies are ideal for rural remote areas.
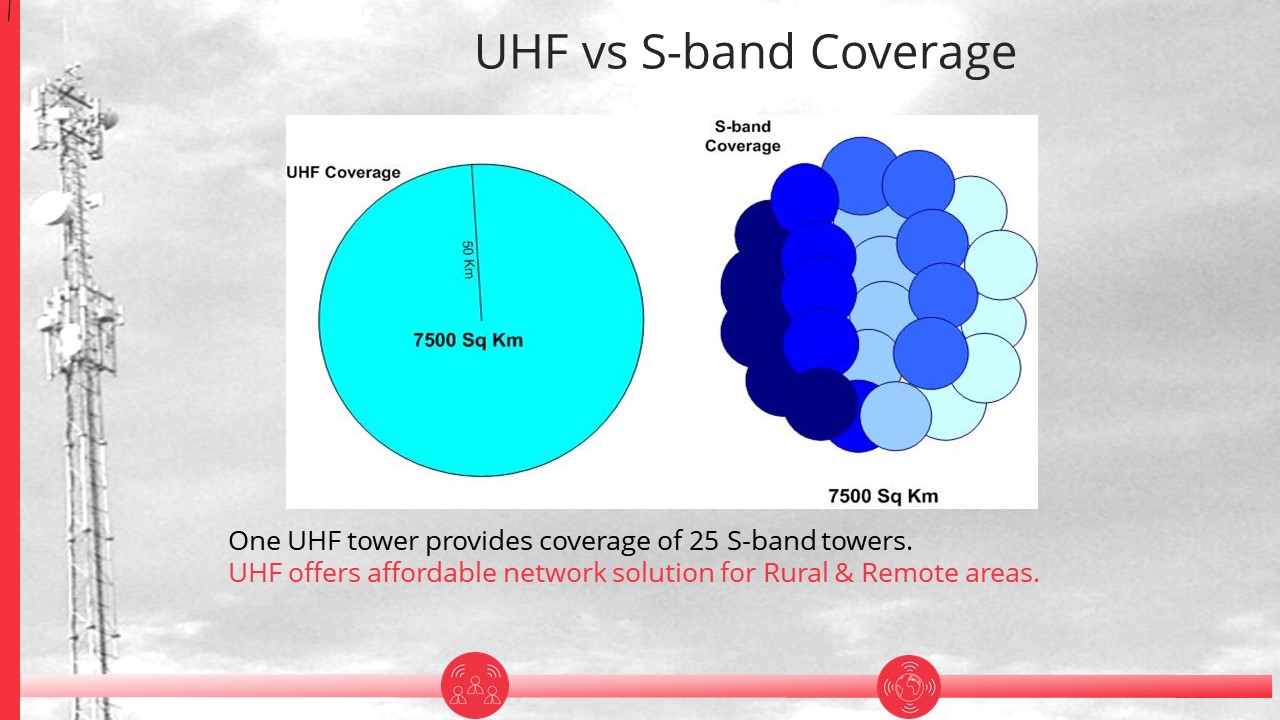
What is the difference between UHF Band and S Band coverage?
One UHF WiDOX 3.1 tower provides coverage of 25 S-band towers. UHF offers affordable network solution for rural and remote areas.
What is the difference in performance between WiDOX 3.1 and TV White Space technologies?
Table below displays the observation between WiDox and all legacy technologies.
| Features | WiDOX 3.1 | Legacy TV-WS |
|---|---|---|
| Base Station Transmitter | 100 W per ch. (50 dBm) | 1 W (30 dBm) |
| Base Station ERP | 1000 W per ch. (60 dBm) | 4 W (36 dBm) |
| CPE Transmitter | 0.5 W (27 dBm) | Mode I 100 mW (20 dBm) |
| CPE EiRP | 10 W (40 dBm) | Mode II 40 mW (16 dBm) |
| Licensed | Yes, protected | No, unprotected |
| Geolocation required | No | Yes |
| Bandwidth | Up to 192 MHz Down, Over 95 MHz Up | Limited bandwidth |
| Control of channels | Total control to add/delete | Limited control |
| Total System Control | Via NOC | Limit4ed Control |
What is adaptive modulation?
Link adaptation, or adaptive modulation and coding (AMC), is a term used in wireless communications to denote the matching of the modulation, coding and other signal, and protocol parameters to the conditions on the radio link (e.g., the path loss, the interference due to signals coming from other transmitters, the sensitivity of the receiver, the available transmitter power margin, etc.)
What is multicasting?
In computer networking, multicasting (one-to-many or many-to-many distribution) is group communication where information is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. WiDOX 3.1 technology allows the delivery of the same multicast data to all subscribers at the same time.
What is DOCSIS
The original definition of DOCSIS is Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification. DOCSIS is one of the most widely deployed transport and physical layer protocols in the world, used in cable TV systems (tens of millions deployed), satellite communication (WildBlue), data over power line, and wireless (WiDox).
What is the difference between EuroDOCSIS and DOCSIS?
EuroDOCSIS uses 8 MHz channels, and DOCSIS uses 6 MHz channels.
What are the benefits of using full duplex DOCSIS 3.0 system for wireless connectivity?
What are the benefits of using full duplex DOCSIS 3.1 system for wireless connectivity?
This is a new generation of cable technology with many benefits.
What is full duplex and half-duplex?
Full-duplex allows simultaneous transmission and reception and maintains consistent high data rate to the edge of service area/distance subscribers, whereas half-duplex allows only transmission or reception to occur and may not maintain full data rate consistently to the edge of service area/distance subscribers. WIDOX 3.1 is a full-duplex solution and MiLTE is a half-duplex solution.